IDTechEx: Market size of weeding robots to increase 11-fold in five years
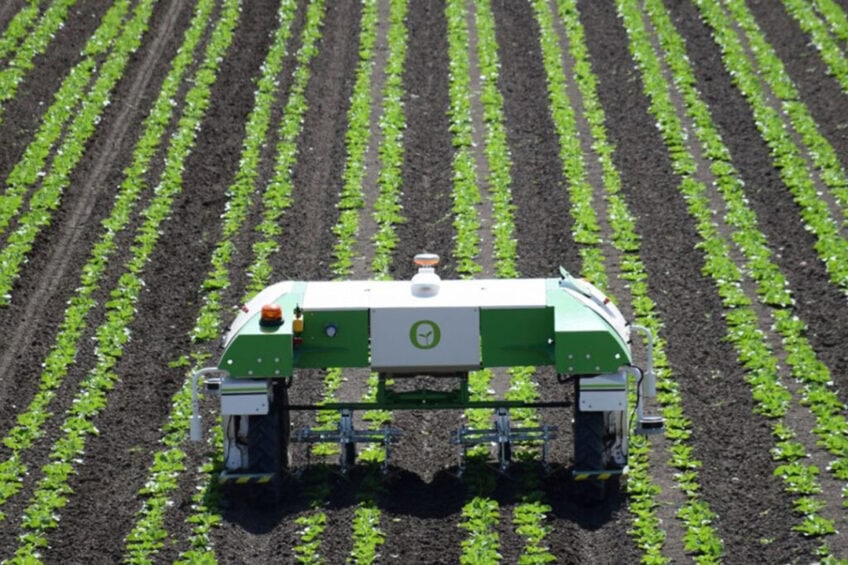

According to market research company IDTechEx, the market size of weeding robots will have an 11-fold increase in the upcoming five years. The demand for ag drones will increase 8-fold over the next ten years.
The market size of weeding robots and spraying drones will accelerate in the coming years, according to IDTechEx’s recent research “Agricultural Robots and Drones 2022-2032: Technologies, Markets & Players”.
The researchers say growth is driven by problems such as water scarcity, overuse of chemicals, decline of biodiversity, greenhouse gas emissions and eutrophication, for which ag robots and ag drones can be a potential solution.
Moving towards variable rate approach
To reduce the use of chemicals and their subsequent negative impacts, precision agriculture has become more and more trendy, say the authors. “With improving technology, farming is gradually moving away from the indiscriminate constant rate approach that historically dominated agriculture towards using a variable rate technology approach.”
Meanwhile, with the disruption of the supply chain, chemicals and fertilizers have become increasingly pricy, encouraging farmers to maximize their resource use and avoid the overuse of chemicals, for example, through mechanical weeding or precise control of the chemical use of each individual plant.
Mechanical weeding ideal use case for automation
Because precision agriculture technology needs a large amount of data collected from plants and crops, it is almost impossible for human beings to collect manually. Meanwhile, the accurate application of chemicals or mechanical weeding also needs precise control, which makes it an ideal use case for automation. Therefore, in order to apply precision agriculture, the use of automation via robots becomes a feasible solution, the IDTEchEx researchers say.
The report states weed control is one of the most common applications for agricultural robots. “Large-scale spraying of herbicides in a constant rate approach is currently the dominant model. The area of the field often determines the rate of spraying, and therefore agrochemicals are often over-applied, leading to unnecessary costs for farmers and accelerating the growth of herbicide resistance. A precision agriculture approach can help overcome these challenges.”
Geolocation and farm mapping alongside GPS-enabled variable-rate sprayers to vary the spraying rate/volume according to the needs of a patch/crop has begun gaining traction in recent years, particularly as technology such as aerial drones and variable rate sprayers become more accessible.
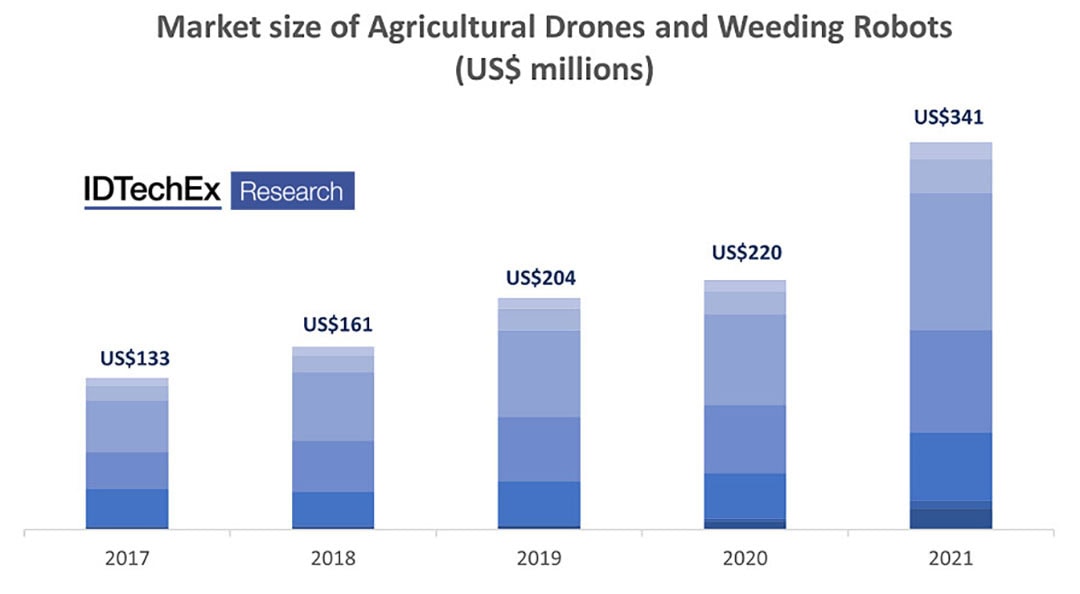
Market size of weeding robots
Agricultural robotics further enable a precision agriculture approach, using computer vision and weed detection algorithms to identify weeds and remove them either mechanically or chemically. IDTechEx’s research shows that the market size of weeding robots was around US$22 million in 2021, and it is expected to have an 11-fold increase in the upcoming five years.
Text continues below graph
Join 17,000+ subscribers
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated about all the need-to-know content in the agricultural sector, two times a week.



