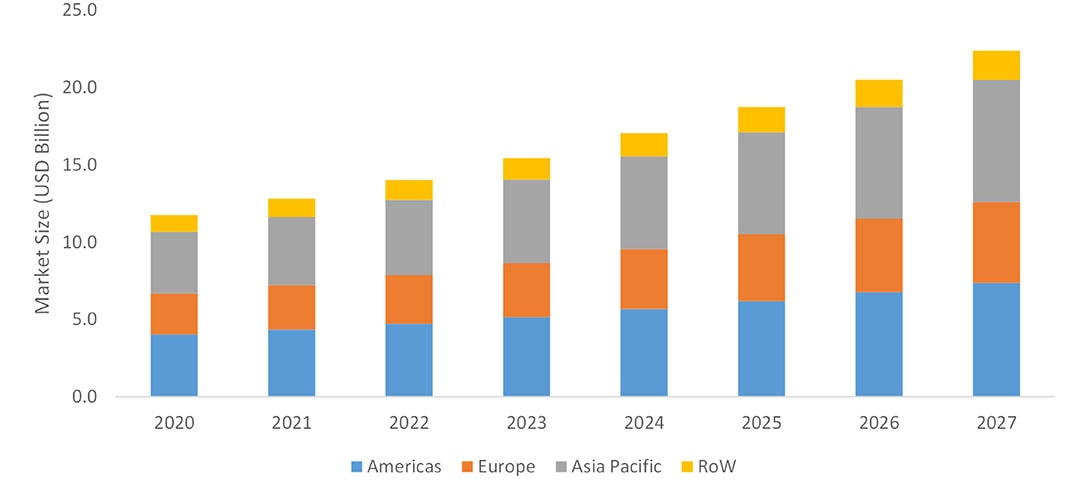
Precision harvesting market to grow to USD 22.4 billion by 2027

Increasing adoption of harvesting robots and autonomous combine harvesters, increasing labour costs and increasing mechanization of farms in emerging countries are driving the growth of the market.
The precision harvesting market is expected to grow from USD 14.0 billion in 2022 to USD 22.4 billion by 2027, at a CAGR of 9.8%, according to a report by MarketsandMarkets.
The most significant factors driving the growth of the precision harvesting market include the increasing adoption of harvesting robots and autonomous combine harvesters, increasing labour costs owing to the shortage of skilled labor, and the increasing mechanization of farms in emerging countries in Asia Pacific and Africa.
Text continues below illustration

Precision harvesting to transform the agricultural sector
Rahul Kumar, author of the report, says precision harvesting has the potential to transform the agriculture sector, making traditional harvesting activities more efficient and economical. Increasing global food demand, extended profitability and crop yield, and minimum wastage of crops during harvesting are the other factors fueling the growth of the market.
Governments in many countries are also helping farmers adopt advanced agricultural and technological tools to improve yield, further boosting the market.
Increasing demand for harvesting robots
The adoption of autonomous harvesting robots and connected devices is expected to increase in the coming years owing to the severe shortage of skilled labor in the horticulture industry and the continual demand for high-quality food.
Researcher Rahul Kumar names various companies that have developed robots to harvest tomatoes, raspberries, and sugar snap peas with minimal human intervention. For instance, Harvest Croo’s robotic harvesters are being tested in Florida; these harvesters employ vision sensors and software to scan plants and locate ripe berries using equipment advanced enough to avoid bruising or damaging the soft fruit.
Similarly, Spain-based Agrobot has been testing a strawberry harvester in Driscoll’s berry field in Oxnard, California, while FFRobotics, an Israeli company, is testing its apple-picking technology in orchards in Washington. FFRobotics claims that its technology can precisely and gently pick 10 times more fruit than an average worker, helping growers reduce costs by supplementing or even replacing human pickers from the dwindling pool of harvesting laborers.
Increasing labour costs
According to Kumar, harvesting robots gained tremendous popularity in recent years owing to increasing labour costs in the horticulture industry and the declining profitability of farms. “Unfortunately, the current technology is not affordable to most farmers. According to a survey by a US-based research agency, less than 3% of growers in the world currently use harvesting robots”, the author states.
However, the gradual reduction in hardware cost coupled with the shortage and steadily increasing cost of labuor is set to increase the adoption of harvesting robots in the coming decades, the report states.
Text continues below illustration
Precision harvesting technology to witness fastest adoption in regions with high labor shortage
Kumar states that almost 50% to 70% of the production cost in horticulture is spent on labor – from harvesting to tasks performed before harvesting, such as weeding, fertiliser application, and site inspection. “Automating these tasks is an extremely important step for large-scale farming operations to ensure profitability.”
Precision harvesting technology improves production efficiency and enables the optimal use of resources, providing farmers additional bottom-line savings, especially in labour costs, the researcher says. “As this has a direct impact on the profitability of farms, the demand for precision harvesting is increasing among farmers.”
He emphasises that autonomous harvesters can perform various tasks, including automatic spraying, weeding, and pruning, besides harvesting. Air and ground robots equipped with sensors can be used to analyze farms and apply the collected data to instruct precision harvesting systems to perform required activities optimally. “Such sensor-equipped harvesting robots are expected to gain tremendous popularity over the next 10 years, subsequently reducing labor costs and increasing the profitability of farms.”
Join 17,000+ subscribers
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated about all the need-to-know content in the agricultural sector, two times a week.



